The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Introduction
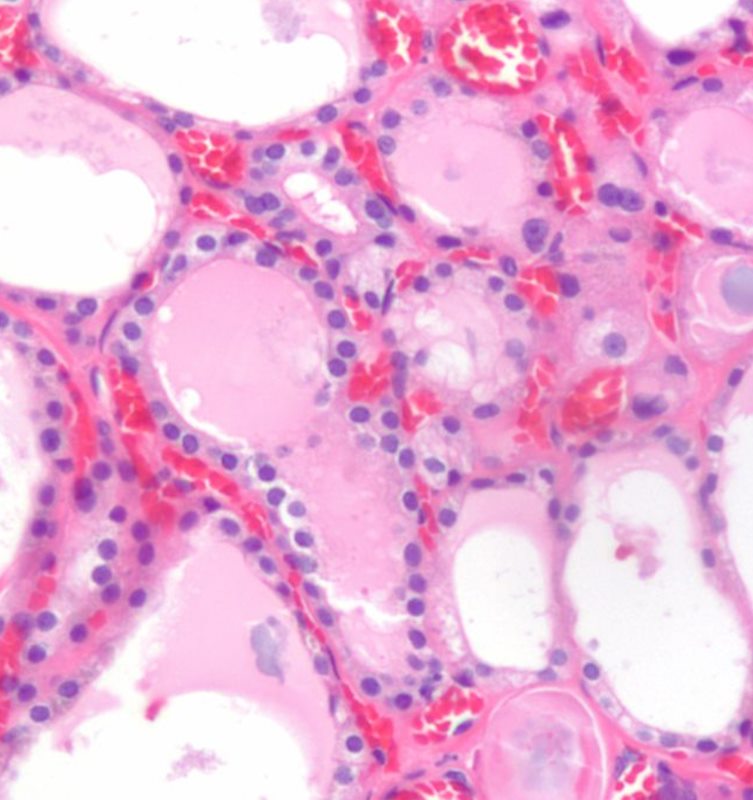
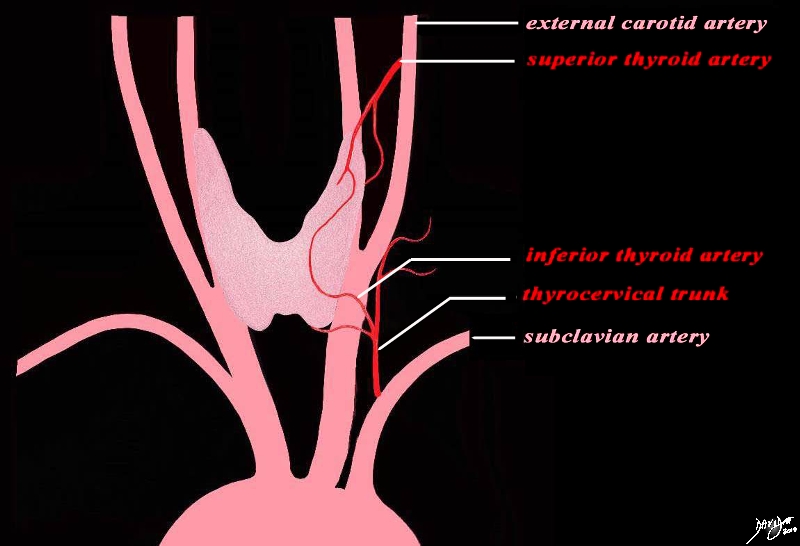
The thyroid receives blood from the superior thyroid artery, which branches from the external carotid artery, the inferior thyroid artery, which branches from the thyrocervical trunk, and the thyroid ima artery, which branches from the brachiocephalic trunk.
Blood Supply of the Thyroid |
|
The blood supply of the thyroid gland comes from tewo sources. the superior thyroid artery arises from the external carotid artery and the inferior thyroid artery arises from the thyrocervical truck which is a branch of the subclavian artery. The two vesels each have an anterior and posterior division and form an anastomoses both anterirly and posteriorly Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 47680d05.8kb03b05b.8Lb01.8s |
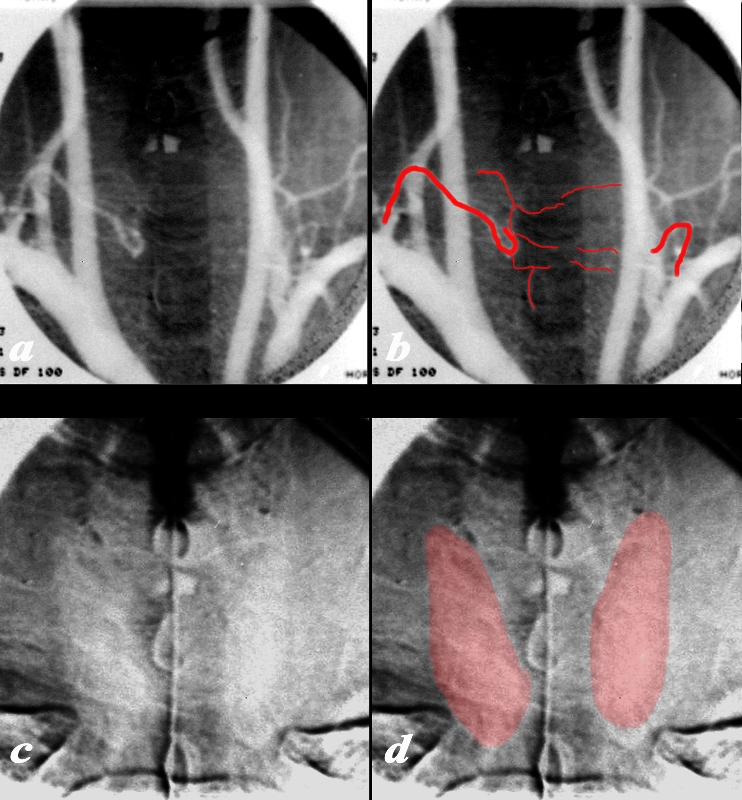
Digital Aortogram Showing Subtle Diffuse Blush of the Thyroid |
|
The arch aortogram injection in the A-P projection of the shows remnants of the right inferior thyroid artery that arises from the subclavian artery (a, and overlaid in b) together with barely seen vessels supplying the thyroid. A small segment of the left inferior thyroid artery is also perceived. In the capillary phase of the angiogram a faint homogeneous blush of thyroid is seen (c and overlaid in d). Courtesy Barry Sacks MD 97215c01.8 |
Superior Thyroid Artery
“The superior thyroid artery’s origin is level with the greater cornu of the hyoid bone, and its end is at the thyroid gland. The vessel travels upward and forward in the carotid triangle, during which it is covered by skin, platysma, and fascia. Then it runs downward, covered by the omohyoid, sternohyoid, and sternothyroid. On its side towards the center of the body is the inferior constrictor of the pharynxas well as the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. The branches of the superior thyroid artery are an infrahyoid branch, a sternocleidomastoid branch, the superir laryngeal artery, and a cricothyroid branch. The infrahyoid branch (ramus infrahyoideus, ramus infrahyoideus arteriae thyroidea superioris, hyoid branch) is a small vessel running along the bottom of the hyoid bone while covered by the thyrohyoideus that unites with the opposite side’s infrahyoid branch. The sternocleidomastoid branch (ramus sternocleidomastoideus, ramus sternocleidomastoideus arteriae thyroideae superioris, sternomastoid branch), which travels down and lateral across the carotid sheath, feeds the sternocleidomastoideus in addition to neighboring muscles and integument. Frequently this vessel originates directly from the external carotid artery. The superior laryngeal artery (arteria laryngea superior) is the largest of the superior thyroid’s branches. In travels with the internal laryngeal branch of the superior laryngeal nerve into the thyrohyoideus and pierces the thyrohoid membrane, feeding the muscles, mucous membrane, and glands of the membrane before uniting with the oposite side’s superior laryngeal artery. In thirteen percent of cases this vessel arises directly from the external carotid artery. The cricothyroid branch (ramus cricothyroideus) is a small vessel that courses across the cricothyroid membrane and communicates with the opposite side’s cricothyroid branch. In sixteen percent of cases, the superior thyroid originates from the common carotid artery.”
The recurrent laryngeal nerve is closely related to the inferior thyroid artery. The nerve may pass anterior, posterior, or through the branches of the inferior thyroid artery.
Selective Angiogram of the Superior Thyroid Artery off the External Carotid Artery |
|
This selective injection in the A-P projection of the superior thyroid artery that arises from the external carotid artery shows a diffuse normal blush of the left lobe of the thyroid Courtesy Barry Sacks MD 97213a.8b |
|
Inferior Thyroid Artery from the Thyrocervical trunk |
|
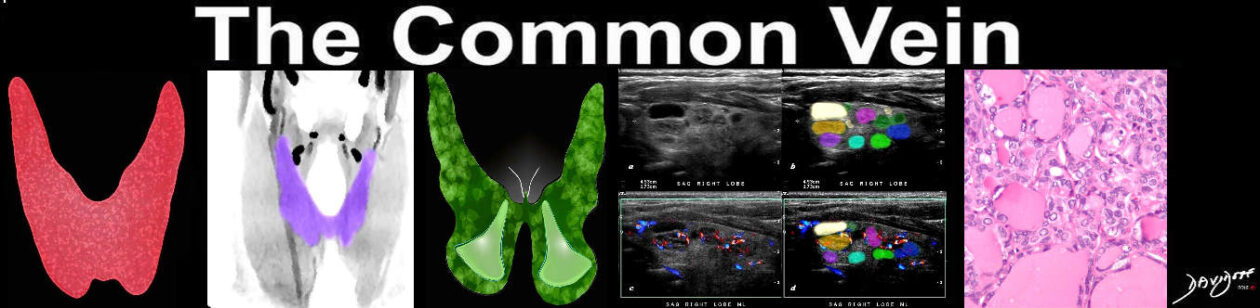
This selective injection in the A-P projection of the inferior thyroid artery (red arrow) that arises from the subclavian artery as a branch of the thyrocervical trunk shows the vessel coursing medially with an early blush in the early arterial phase, followed by a diffuse blush in the capillary phase. Courtesy Barry Sacks MD 97218c.81 |
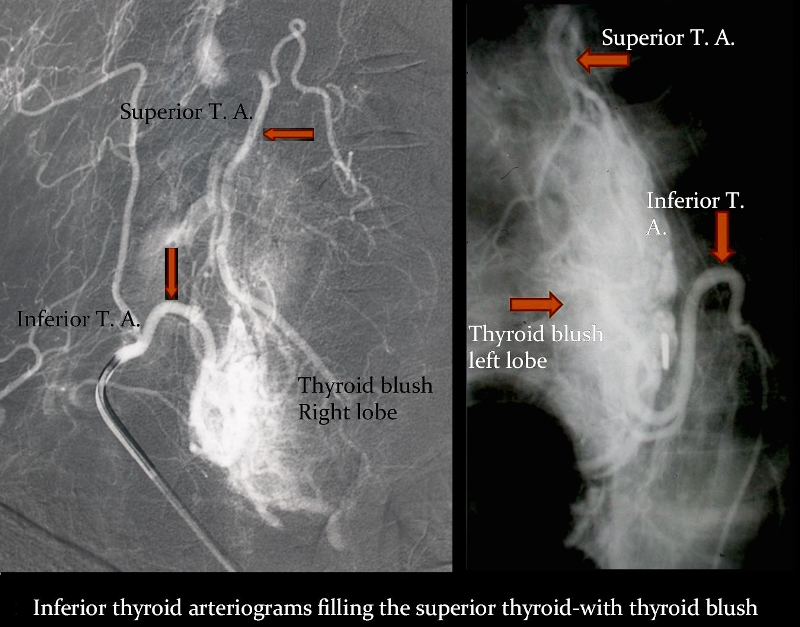
Collateral Pathway between Superior and Inferior Thyroid Circulaltions |
|
These angiograms demonstrate the collateral connections between the inferior and superior thyroid arteries. In image (a) the selective injection of the right thyrocervical trunk shows filling of the superior thyroid artery cinforming their intimate connection and collateral capability. In the second case of selective injection of the left inferior thyroid artery, filling of the superior division is seen as well with large collateral pathways visible (barely) inside the thyroid). Courtesy Barry Sacks MD 97219d01 |
|
Capillary Network Around the Follicles |
|
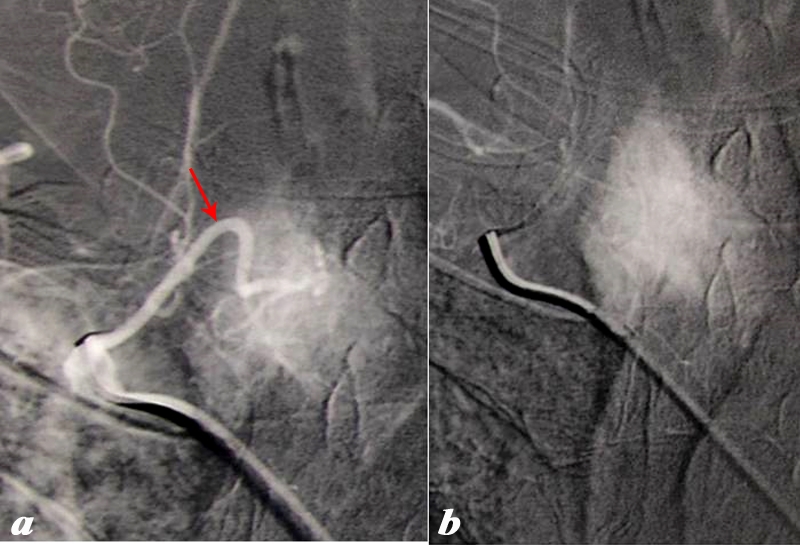
The histological section using H&E stain shows normal thyroid tissue with a focus on a bilobed follicle toward left of centre. The cuboidal epithelium is exemplified in this follicle. An extensive capillary network in close association with the glandular tissue is typical of an endocrine organ. The capillaries are identified by the red cells lined up within the vessel lumen. Image Courtesy Ashraf Khan MD. Department of Pathology, University of Massachusetts Medical School. 99412d |
Ultrasound Evaluation
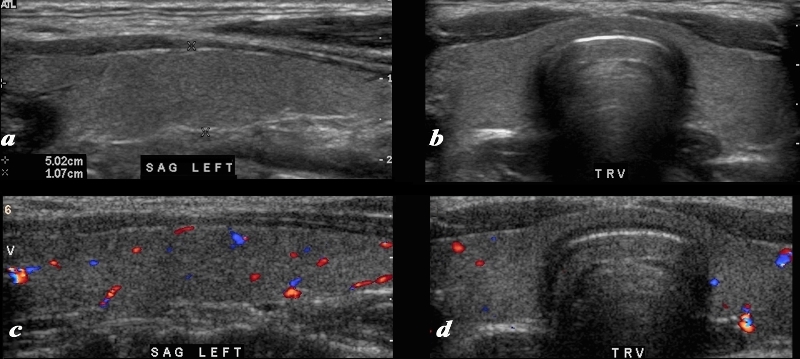
Intraparenchymal Blood Flow |
|
A normal ultrasound of the thyroid gland is demonstrated. Image a and b are sagittal and transverse images, and images c and d are comparable views with color flow Doppler. The normal ultrasonographic characteristics demonstrating size shape position and character of the thyroid and normal color flow pattern is well demonstrated. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 93832c02L.8 |
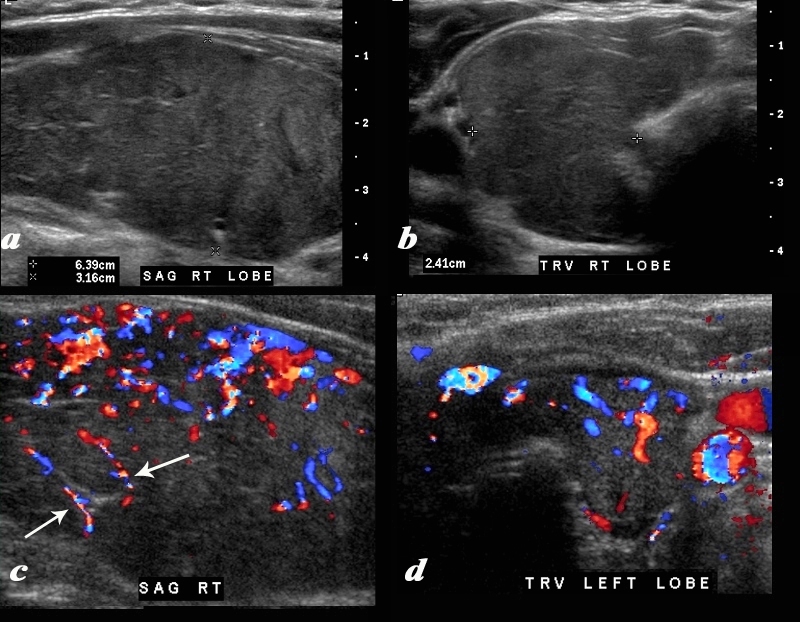
Thyroiditis – Enlargement, Fibrous Strands, and Hypervascularity |
|
A diffusely enlarged, heterogeneous thyroid gland is seen in this 30 year old hypothyroid female patient. The thyroid measures 6.4cms (craniocaudad), by 3.2cms (A-P) by 2.4cms (transverse). Clinical findings were consistent with thyroiditis, with biochemical findings suggesting hypothyroidism. The sagittal view shows coarse heterogeneous echo texture with fine white bands consistent with fibrosis. The increased vascularity is seen throughout the gland (c,d), but is also seen particularly along some of the bands in the posterior aspect of the gland (c arrows). The enlarged gland in the transverse dimension is almost round. (b). This rounded shape in the transverse dimension is a clue to the presence of the enlarged gland, even before the measurements are taken and evaluated. The findings are consistent with a thyroiditis. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 94583c01.8 |