The Common Vein
Copyright 2010
Introduction
The thyroid gland is the first endocrine gland to develop in the embryonal stage at approximately the 24th day of gestation as an outpouching at the base of the tongue in the foramen cecum on the median surface of the developing pharyngeal floor. It takes its origin from the medial anlage which derives from the floor of the foregut. The medial anlage forms the major portion of the thyroid. The thyroid gland grows and descends anterior to the trachea. As it descends it remains attached to the thyroglossal duct which normally degenerates. Thje thyroid gland reaches its final position in the seventh gestational week overlying the second to fourth tracheal rings. Thereafetr it grows laterally to form two lobes.
If the caudal end of the thyroglossal duct persists it becomes the pyramidal process.
Applied Biology
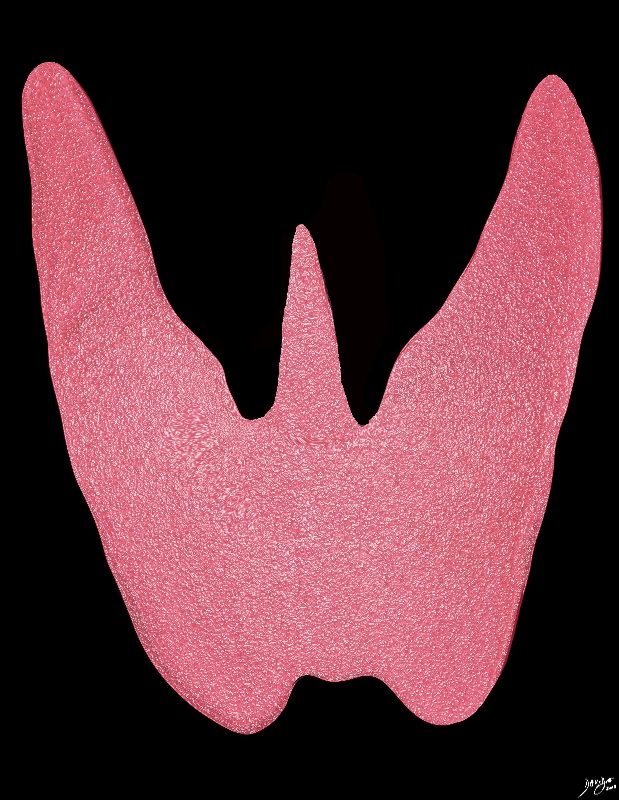
Pyramidal Lobe |
|
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland with two lobes, each looking like an inverted cone. A variation in this shape is a third small cone that lies between the lobes and sometimes originates off one of the lobes more commonly the left. This is called a pyramidal lobe and is an embryological remnant of the thyroglossal duct. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 93852.4kd02b02g.8s |
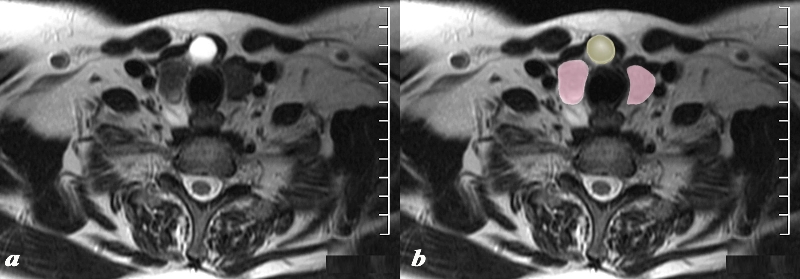
Thyroglossal Cyst |
|
The MRI T2 weighted image through the inferior aspect of the thyroid gland (pink) shows a cystic structure (yellow), intensely T2 bright (a), in the region of the isthmus in the ventral and midline position of the gland. Findings are consistent with a thyroglossal duct cyst Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 97310cL.8 |