The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Introduction
The Butterfly Shaped Organ |
|
The butterfly shaped form of the thyroid gland is appreciated in this image. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93816d02.2kd07b10b.8s |
Butterfly in Sepia |
|
The butterfly shaped form of the thyroid gland is appreciated from a more subtle perspective in this sepia rendering Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93816d02.2kd07b10b05.8s |
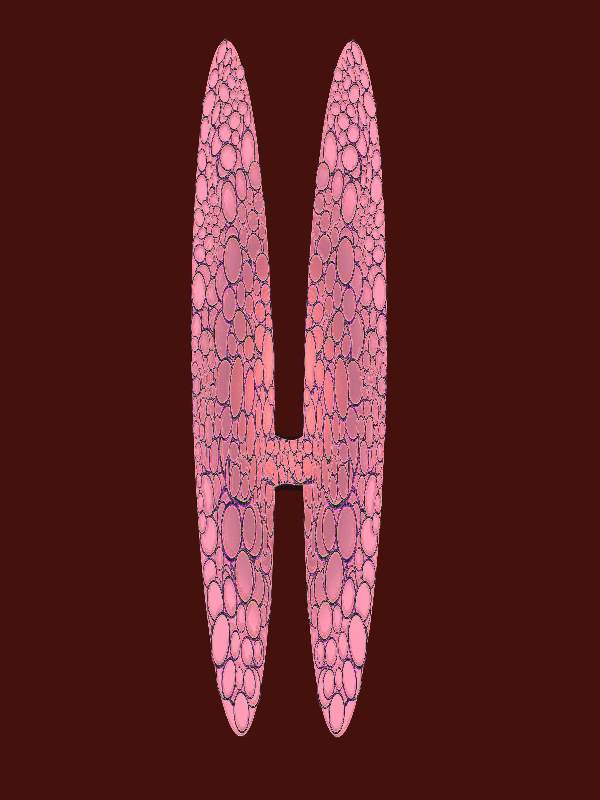
The Normal Thyroid |
|
The H shaped form of the thyroid gland is appreciated in this image. The isthmus may be broad in its craniocaudad dimension or may be relativel narrow. In the anetroposterior dimension it is only about 3-5mm thick Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93852..4kd02b.8s |
Thyroid Moods |
|
Thyroid Moods Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93852.d03cdc04b.81s |
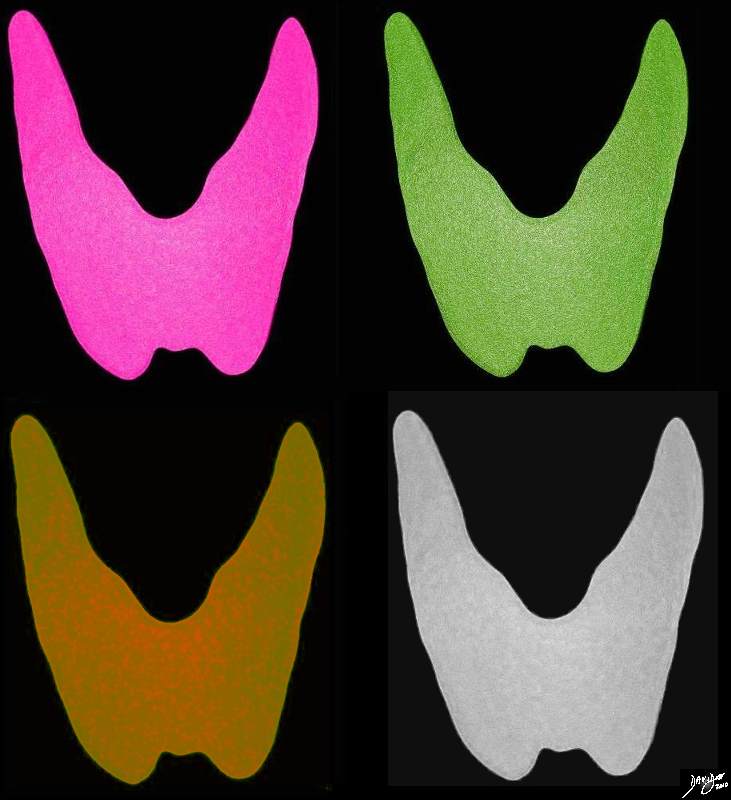

A Thyroid for All Seasons |
|
A thyroid for all seasons Spring – pink summer green fall orange winter gray Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93852.d03cdc04b.41k.8s |
|
Artistic Rendition Showing the Combined Macroscopic and Microscopic Features |
|
The normal gland has a unique appearance both macroscopically and microscopically. Its name implies a shield like shape, and it mirrors the shape of the thyroid cartilage. It is brownish red in color and at a histological level is made of variably sized rounded glandular rosettes with spaces that contain colloid in which thyroglobulin is stored. Thyroglobulin is a precursor of the thyroid hormones.. Storage of endocrine products outside of the cell is a unique feature of the thyroid gland. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94460b13t06p04.81s |
The Thyroid Gland – Unique Appearance |
|
Artistic rendition of the normal thyroid gland The histological make up of the thyroid has a unique appearance consisting of variably sized rounded glandular rosettes with spaces that contain a homageneously pink materail called colloid, subtended by a basal layer of cells that secrete the colloid. This diagram shows these rosettes which in fact make up the whole gland. The base of the rosettes contain a single layer of an epithrlium almost cuboidal cells that secrete the colloid (shown in navy blue) Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94460b02d17.8s |

Massive Non Toxic Multinodular Goiter |
|
This 75 year old male presents with an asymptomatic multinodular goiter, consisting many nodules of varying size and density, some with macrocalcifications as seen by coronal CT reconstruction (a,b) and axial images (c,d). The windows of the CTscan have been narrowed (a,c), to enhance the morphological characteristics of the components of retrosternal goiter. Each lobe of the thyroid measures about 12 cms in sagittal 6cms. in transverse and 12cms in A-P dimension. These findings are consistent with a non toxic multinodular goiter. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 94712c01L01.8s |
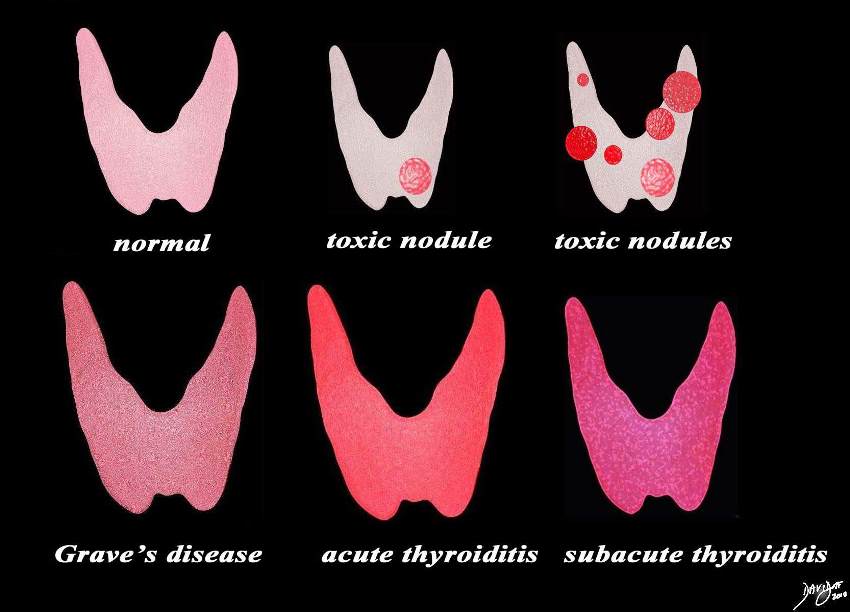
Thyrotoxicosis |
| This diagram shows the structural possibilities in a patient who presents with thyrotoxicosis. Reading from upper left the normal thyroid is shown for reference of size and normal activity (pink). Next is the single toxic nodule that suppresses the function of the gland and the also causes the rest of the gland to shrink. This is followed by a diagram of multiple toxic nodules and the gland in this case may also be smaller than normal. The lower series of images include Grave’s disease, which is the most common cause of thyrotoxicosis, followed by acute thyroiditis and then subacute thyroiditis.
Courtesy Ashley DAvidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93852.d03cdc06.8s |
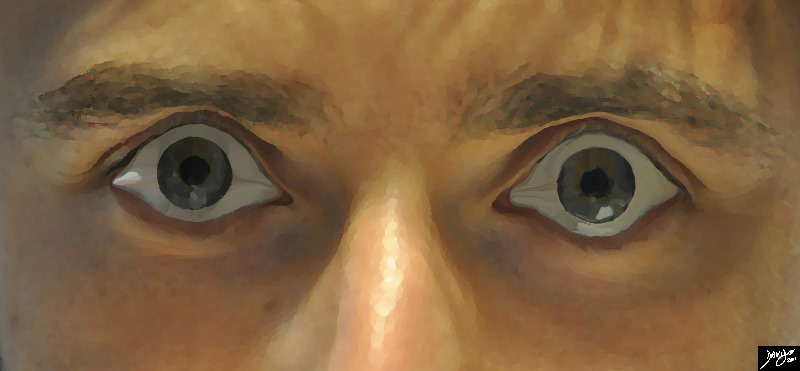
Exopthalmos and Grave’s Disease |
|
Bilateral exopthalmos or bulging of the eyes is most commonly associated with Grave’s disease which is an autoimmune disease associated with thyrotoxicosis. Upperlid retraction results in the ability to see the whites of the eyes on both sides of the iris. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2011 100169pb03b |
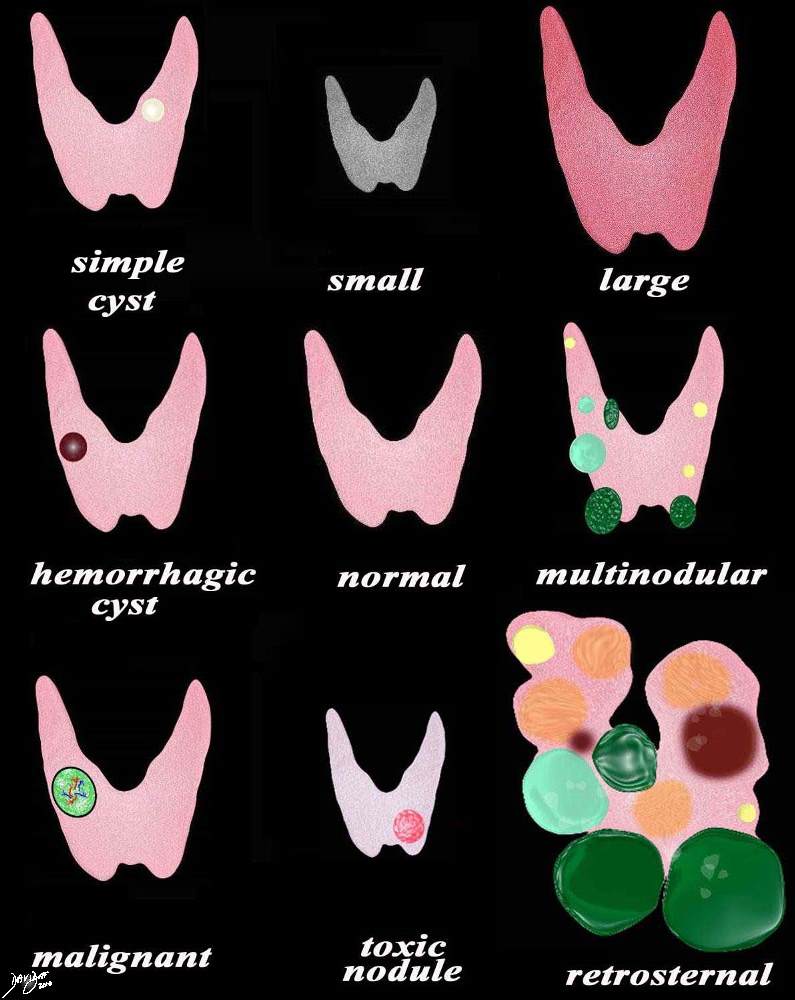
Changes in Disease |
|
A variety of appearances of the thyroid gland in disease including (from top left to right a simple cyst (yellow) the small atrophied gland seen in hypothyroidism, the large hyperemic gland seen in acute thyroiditis and Graves disease, the hemorrhagic cyst (maroon) normal, multinodular goiter of cysts (yellow), heterogeneous (light green) and solid (dark green), the malignant nodule, hot nodule with secondary atrophy of the gland, and the large multinodular retrosternal gland. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93852e07.9s |
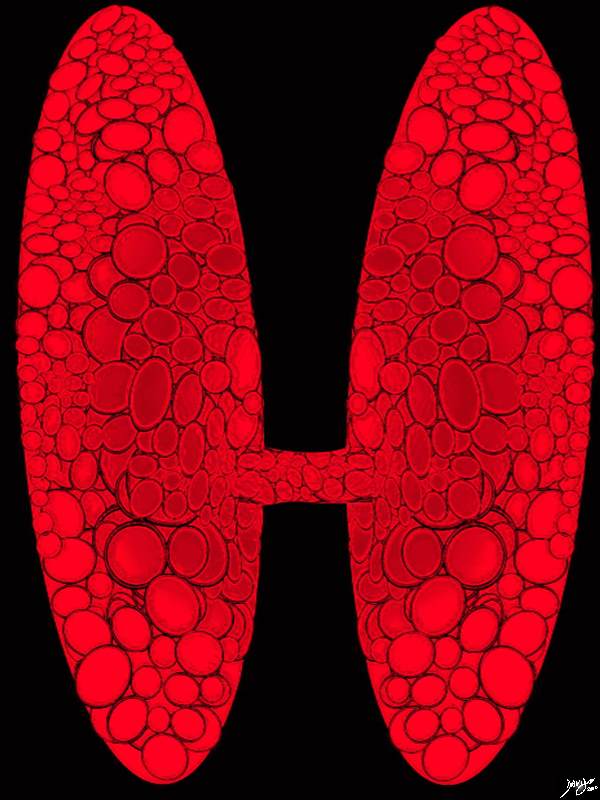
The Normal Sized Thyroid Gland |
|
The normal sized thyroid gland Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94460b13b05b02bb02b.8s |
Thyrotoxicosis |
|
The diffusely hyperactive gland is enlarged and hypermetabolic Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94460b02d14b01.8S |
The Diffusely Enlarged Gland |
|
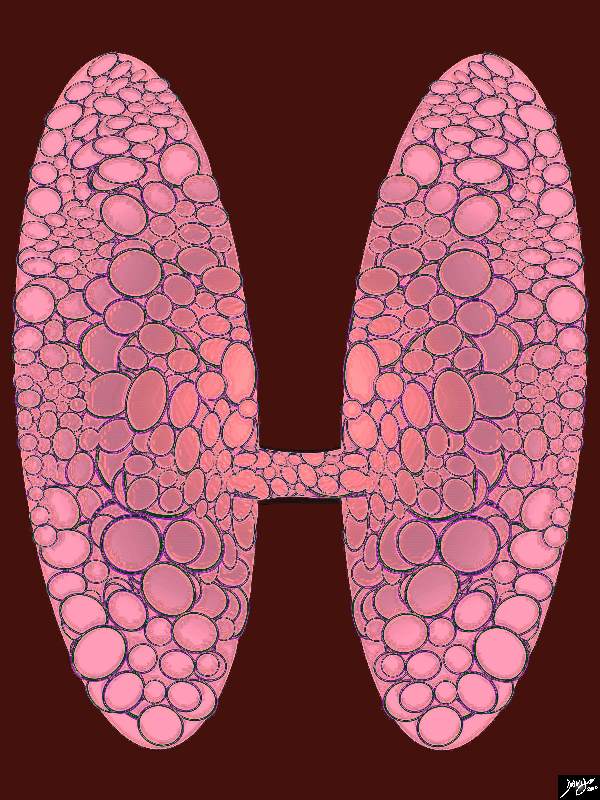
Enlarged thyroid gland The histological make up of the thyroid shows an overall increase in the volume of the thyroid with the individual glands still being normal – just more of them resulting ina rotund appearance This appearance would be in keeping with an acute thyroiditis where the gland has become swollen. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94460b13b05b02.81s |
Acute Thyroiditis |
|
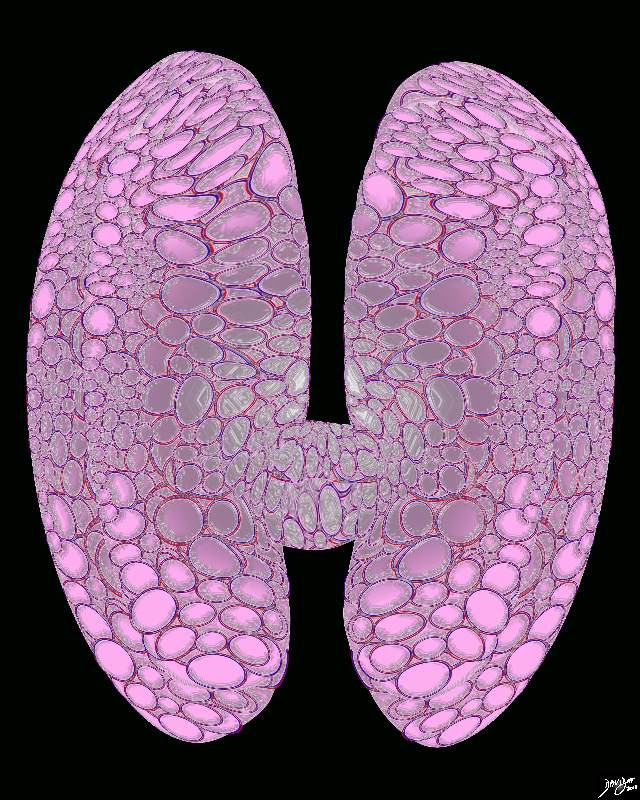
Enlarged thyroid gland The histological make up of the thyroid shows an overall increase in the volume of the thyroid with the individual glands still being normal – just more of them resulting ina rotund appearance This appearance would be in keeping with an acute thyroiditis where the gland has become swollen. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94460b15.8s |
Multinodular Goiter |
|
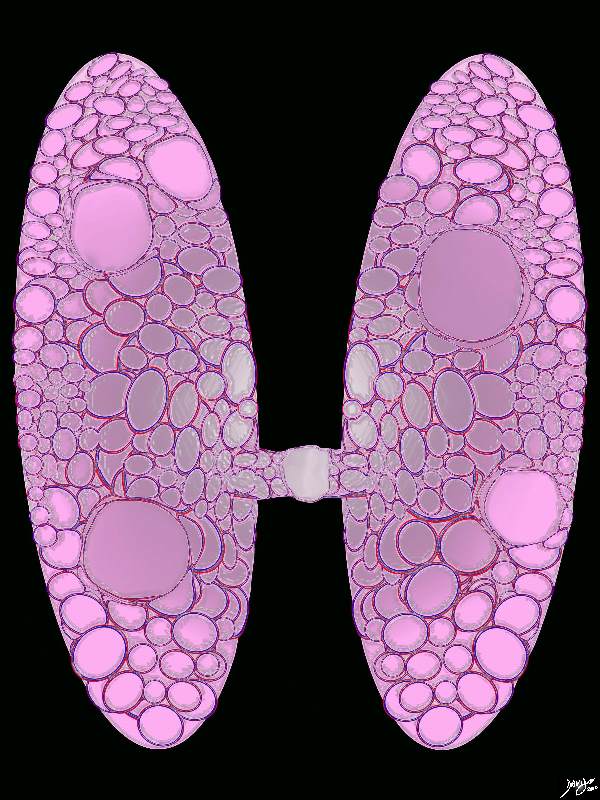
Enlarged thyroid gland Several large nodules of varying size are scattered throughout the gland. This basic appearance is characteristic of a multinodular goiter. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94460b16b.8s |
Small Thyroid Gland |
|
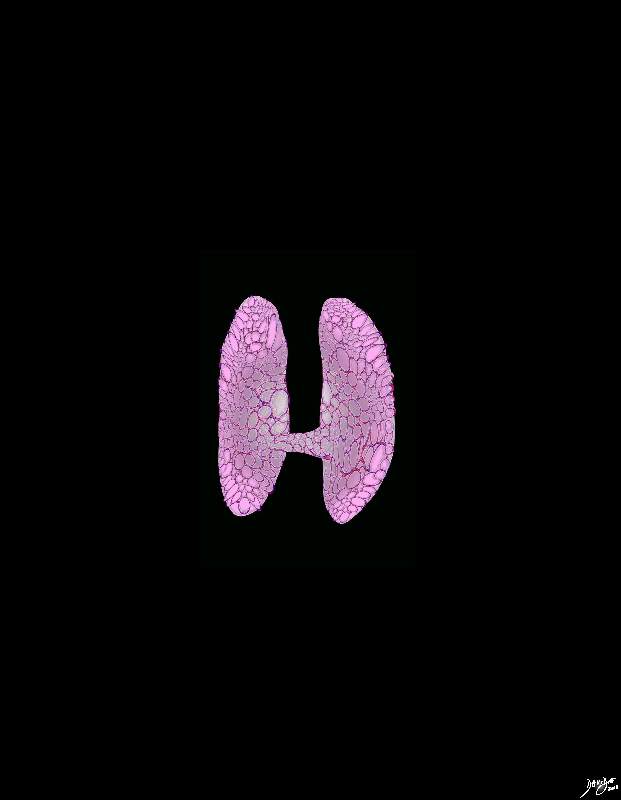
Small thyroid gland The thyroid gland is depicted as a small shrunken gland characteristsic of entities such as end stage thyroiditis and myxedema. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 94460b17.8s |
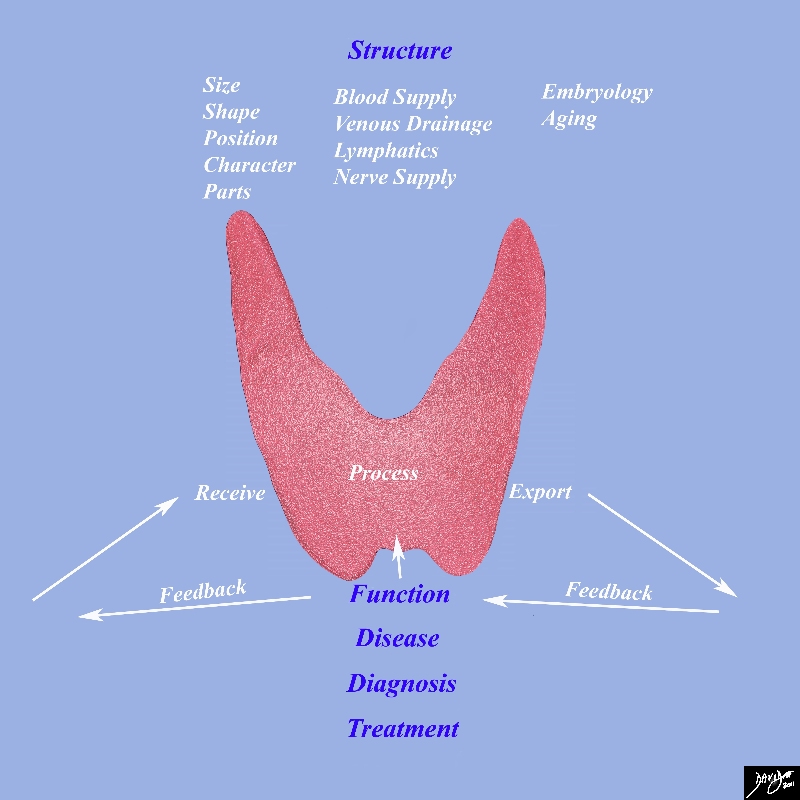
Foundation Principles |
|
This diagram frames the underlying principles and approach to the thyroidin this module Image Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 93852g05c.8s |