The Common vein Copyright 2010
Definition
Acute thyroiditis is an acute suppurative inflammation of the thyroid gland.
Acute thyroiditis is caused by a bacterial infection, usually in patients with septicemia or acute bacteiral endocarditis.
The bacterial infection results in pyogenic infection, with local redness, pain and swelling. The thyroid can be exquisitely tender and the skin overlying the gland is often warm and red.
Structurally there can be abscess formation in the gland.
Functional changes result from systemic and local infection.
Clinically acute thyroiditis presents in a patient with fever and acute bacterial illness. The anterior neck is tender, especially over a swollen thyroid. Redness is apparently over the gland.
Laboratory abnormalities reflect an underlying infection, with increased white blood cell count and left shit. Thyroid function tests are usually normal.
Useful imaging in acute thyroiditis is essentially limited to thyroid ultrasound, which can demonstrate abscesses. Radioactive thyroid scanning is not indicated because the results are normal.
Diagnosis is usually evident from local neck symptoms and underlying infection.
Treatment of acute thyroiditis includes antibiotic therapy to treat the underlying infection and prevent abscess formation. Surgery with incision and draining may be necessary, especially if an underlying embryologic abnormality like an infected thyroglossal duct cyst is found.

Acute Thyroiditis |
|
The acutely inflammed and enlarged gland presents with painful symptoms sometimes associated with hyperthyroidism consistent with acute toxic thyroiditis Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93852.d03.81sd |
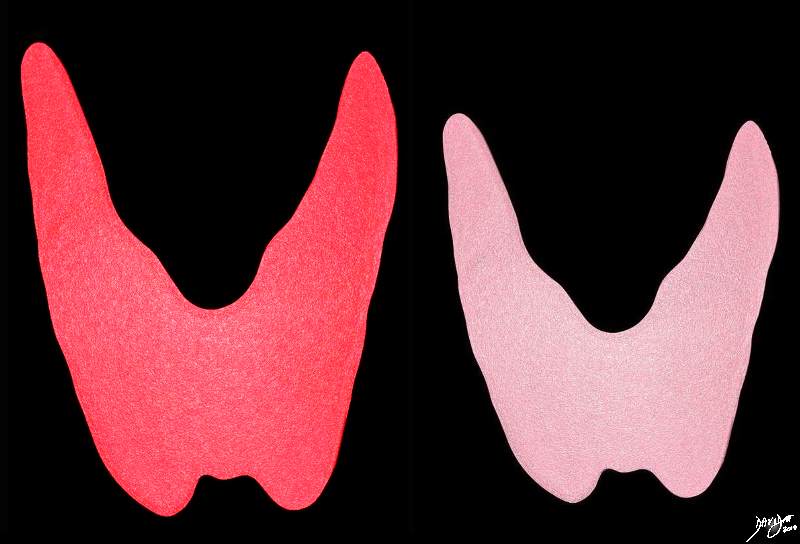
The Inflammed Gland (left) and the Normal Gland (right) |
|
The acutely inflammed and enlarged gland presents with painful symptoms usually not associated with hyperthyroidism. The reddened and enlarged thyroid gland is shown next to the normal gland(pink) Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93852.d03cd.8s |