The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Introduction
Macrofollicular morphology is a normal finding
Histology
|
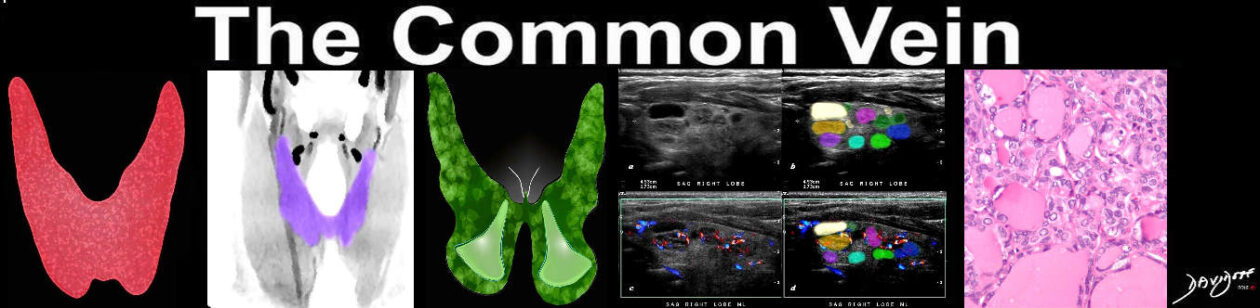
Follicles – Normofollicular and Macrofollicular 10X H& E |
|
The histological section at 10X magnification using H&E stain shows normal thyroid tissue with normofollicular and macrofollicular changes. The single layer of epithelium surrounding the follicle is made up of a simple cuboidal cells and the lumen is filled with pink staining colloid. Thyroglobulin and iodide are contained within the colloid and are used to produce thyroid hormones including thyroxine. Between the cells are the parafollicular cells that produce calcitonin. Image Courtesy Ashraf Khan MD Department of Pathology, University of Massachusetts Medical School. 99411.8 |
Each follicle is lined by a single layer of follicular epithelial cells, collectively termed the follicular epithelium, whose morphology ranges from cuboid when inactive to columnar when active. These cells trap iodine from the bloodstream and use it to synthesize thyroxine and triiodothyronine from the glycoprotein thyroglobulin. If not needed immediately these hormones remain stored in thyroglobulin and are secreted along with colloid into the follicles. When serum levels of thyroxine and triiodothyronine drop too low colloid is absorbed back into the thyroid cells where thyroglobulin is cleaved and the hormones are released through the base of the cell into the surrounding capillaries.
Parafollicular cells surround the follicular epithelium and follicles and synthesize calcitonin, which help regulate calcium metabolism in conjuction with the parathyroid glands.
|
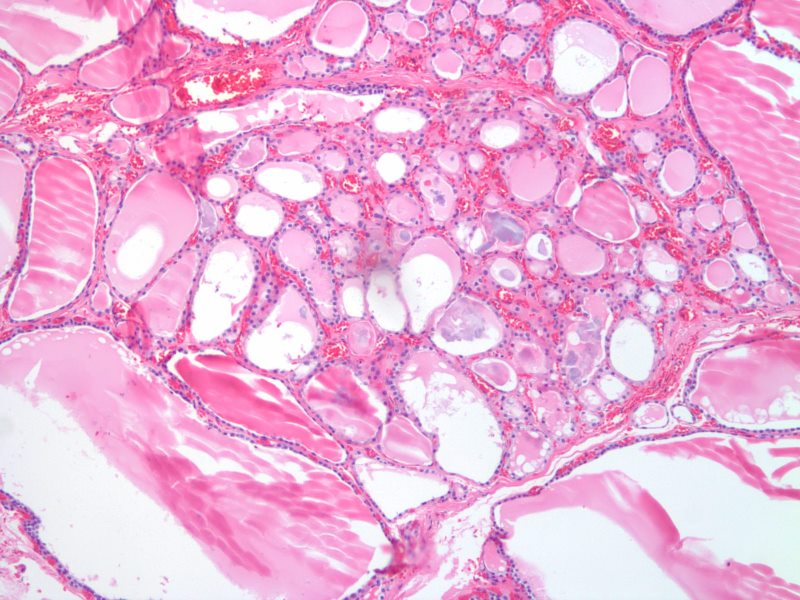
Transitional Epithelium Follicles, Colloid, and Parafollicular Cells 20X H&E |
|
The histological section at 20X magnification using H&E stain shows normal thyroid tissue with normofollicular and macrofollicular changes. The single layer of epithelium surrounding the follicle is made up of a simple cuboidal cells and the lumen is filled with pink staining colloid. Thyroglobulin and iodide are contained within the colloid and are used to produce thyroid hormones including thyroxine. Between the cells are the parafollicular cells that produce calcitonin. Image Courtesy Ashraf Khan MD. Department of Pathology, University of Massachusetts Medical School. 99412.8b02 |
Normofollicles and Macrofollicles
|
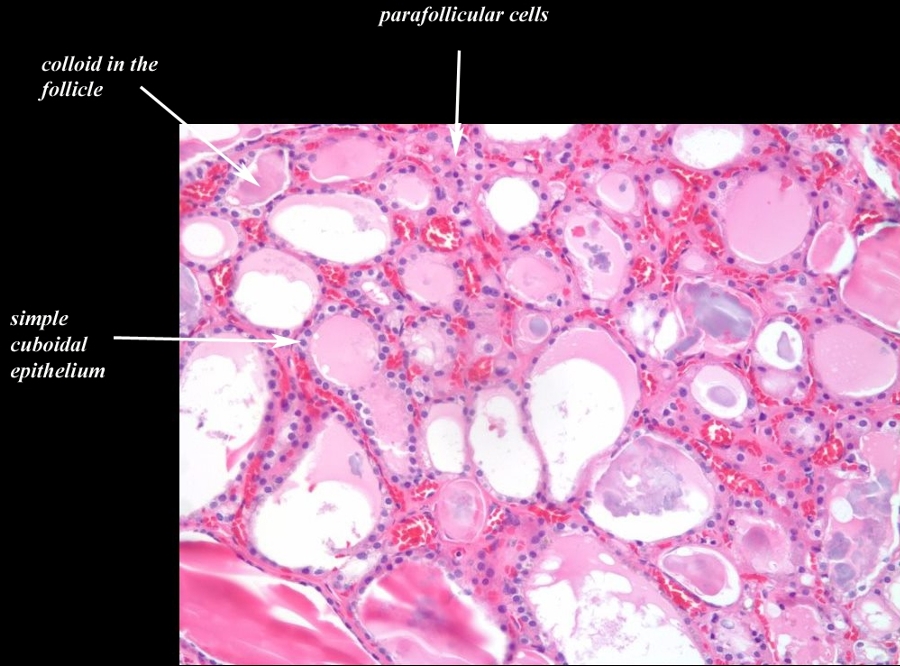
Normal Follicular Appearance Normofollicles and Macrofollicles 20X H&E |
|
The histological section at 20X magnification using H&E stain shows normal thyroid tissue with normofollicular and macrofollicular changes. The single layer of epithelium surrounding the follicle is made up of a simple cuboidal cells and the lumen is filled with pink staining colloid. The different sizes of the follicles is a normal appearance and has no pathological implications. Thyroglobulin and iodide are contained within the colloid and are used to produce thyroid hormones including thyroxine. Between the cells are the parafollicular cells that produce calcitonin. Image Courtesy Ashraf Khan MD. Department of Pathology, University of Massachusetts Medical School. 99410.81 |
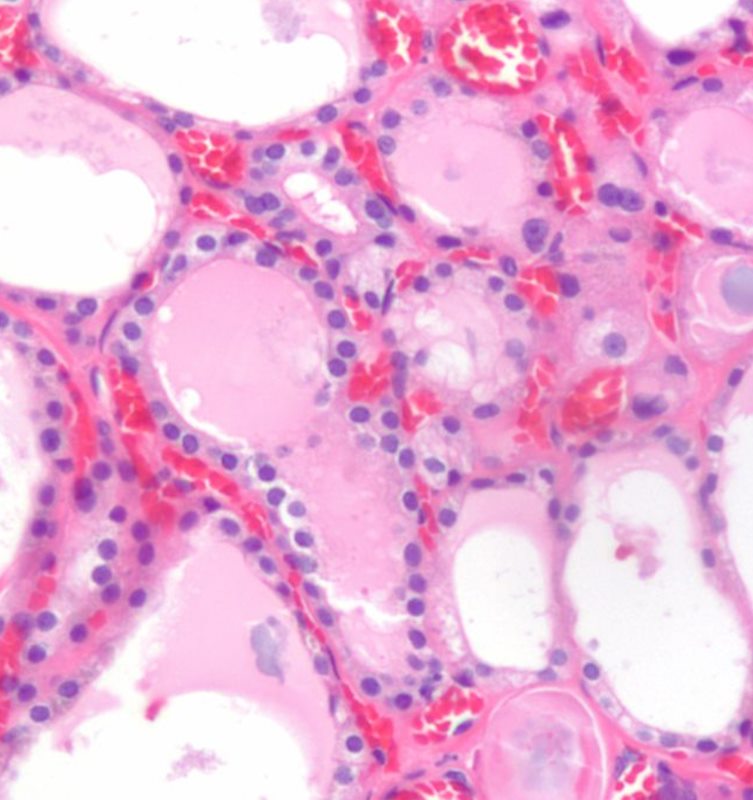
Epithelium and Capillary Network
|
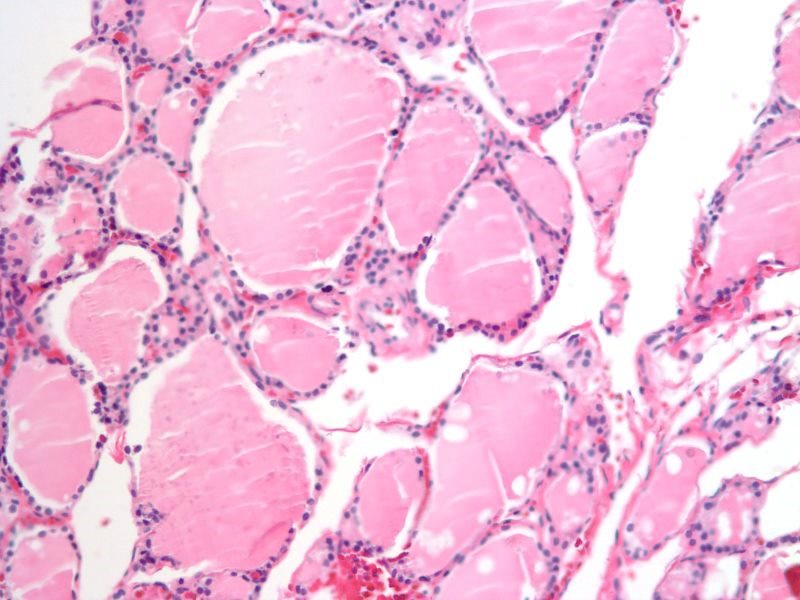
Epithelium and Capillary Network |
|
The histological section using H&E stain shows normal thyroid tissue with a focus on a bilobed follicle toward left of centre. The cuboidal epithelium is exemplified in this follicle. An extensive capillary network in close association with the glandular tissue is typical of an endocrine organ. The capillaries are identified by the red cells lined up within the vessel lumen. Image Courtesy Ashraf Khan MD. Department of Pathology, University of Massachusetts Medical School. 99412d |
Imaging of Nodules with Macrofollicular Histology

Macrofollicular Adenoma |
| 97199b01cg.8 Courtesy Barry Sacks MD |

Cystic and Solid Components of a Macrofollicular Lesion |
| 97199d01c Courtesy Barry Sacks MD |