The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Definition
Hypothyroidism is a disease state in which there is an underproduction of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) by the thyroid gland.
Hypothyroidism can be caused by infection, trauma, autoimmune disease, or nutritional deficiency.
Thyroid gland dysfunction results in a decreased level of circulating T3 and T4, despite increased TSH.
Structural changes will depend on the cause of hypothyroidism, ranging from enlarged inflammatory gland of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis to an atrophic or absent thyroid gland.
Functional changes define the disease and result in a decreased levels of production and circulation free thyroid hormones.
Clinically, a decreased level of thyroid hormones will present with a constellation of symptoms including fatigue, cold intolerance, constipation, depression, and weight gain.
Imaging modalities are not typically used to diagnose hypothyroidism.
Diagnosis is best made with laboratory studies showing high levels of TSH with inappropriate corresponding low levels of circulating T3 and T4.
Treatment for hypothyroidism is replacement of the deficient levels thyroid hormones with synthetic forms such as synthetic T4 (Levothyroxine) or combination T4 and T3 replacement. Treatment adequacy is determined by monitoring TSH levels to ensure adequate physiologic levels are achieved and maintained.
|
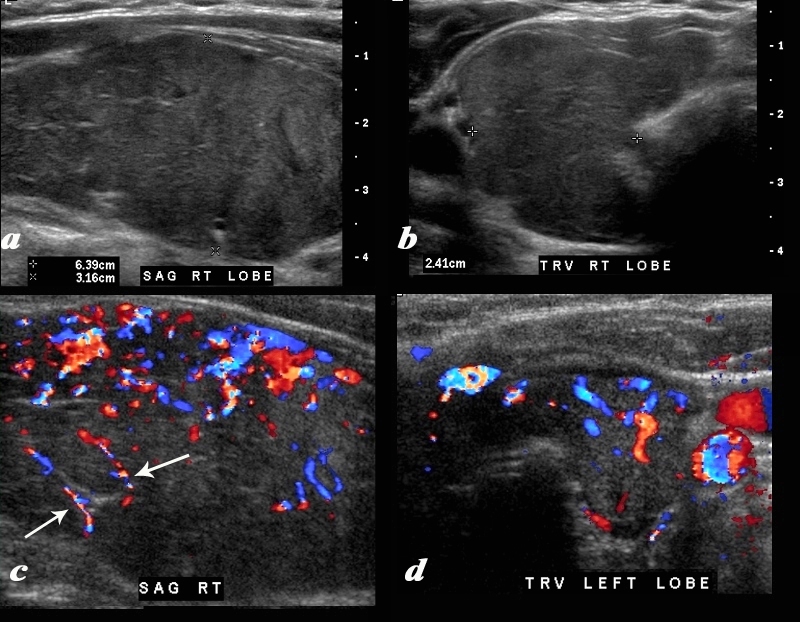
Hypothyroidism with Enlarged Hypervascular Gland and Coarse Strands |
|
A diffusely enlarged, heterogeneous thyroid gland is seen in this 30 year old hypothyroid female patient. The thyroid measures 6.4cms (craniocaudad), by 3.2cms (A-P) by 2.4cms (transverse). Clinical findings were consistent with thyroiditis, with biochemical findings suggesting hypothyroidism. The sagittal view shows coarse heterogeneous echo texture with fine white bands consistent with fibrosis. The increased vascularity is seen throughout the gland (c,d), but is also seen particularly along some of the bands in the posterior aspect of the gland (c arrows). The enlarged gland in the transverse dimension is almost round. (b). This rounded shape in the transverse dimension is a clue to the presence of the enlarged gland, even before the measurements are taken and evaluated. The findings are consistent with a thyroiditis. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 94583c01.8 |
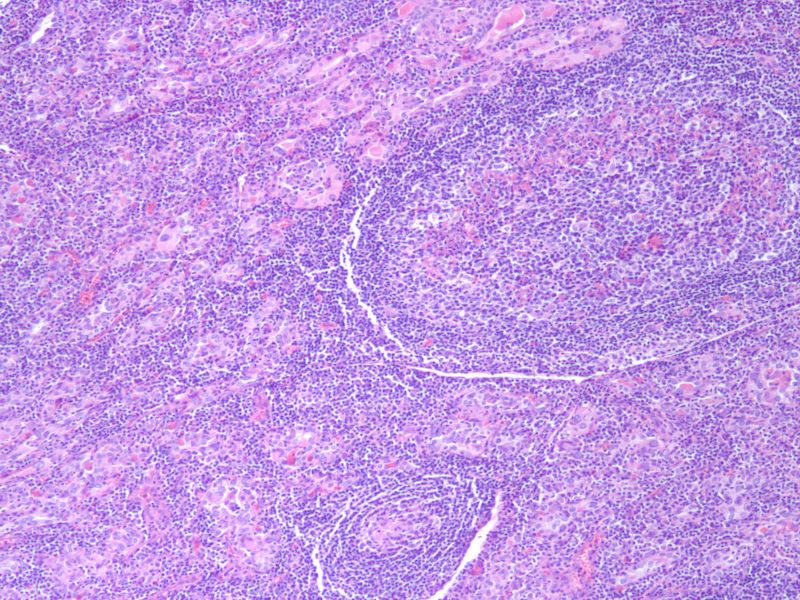
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis – Atrophic Follicles Lymphocytic Infiltrate 10X H&E |
|
The histological section at 10X magnification using H&E stain shows atrophic follicles with Hurthle cell change and dense lymphocytic infiltrate in the stroma Image Courtesy Ashraf Khan MD. Department of Pathology, University of Massachusetts Medical School. 99401.8 |
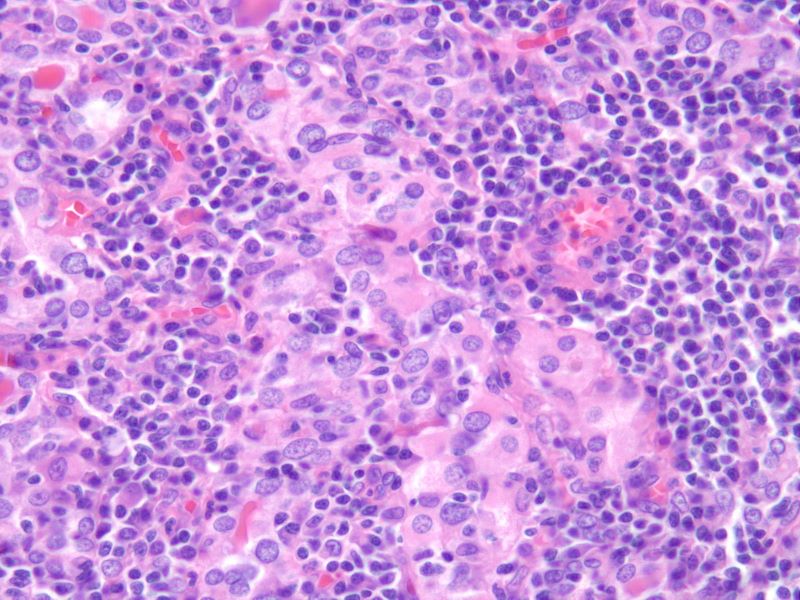
Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis – Atrophic Follicles, Hurthle Cells, Lymphocytic Infiltrate 40X H&E |
|
The histological section at 40X magnification using H&E stain shows atrophic follicles with Hurthle cell change and dense lymphocytic infiltrate in the stroma Image Courtesy Ashraf Khan MD. Department of Pathology, University of Massachusetts Medical School. 99402.8 |